Posts tagged stated preference
Impacts of replacing a fixed transit line by a Demand Responsive Transit system
The diffusion of the smartphone and the urban sprawl is pushing both private and public actors to revisit the concept of the demand-responsive transit (DRT). Mokumflex is a DRT pilot program that replaced the regular bus service in low-density areas of Amsterdam, the Netherlands, for 12 months. The close collaboration with the private enterprise that conducted the system but also with the local bus operator allowed the authors to have access to precise databases, giving this article empirical information for both the situation before and after the implementation. These insights help to understand DRT systems and support (future) design of DRT and transit systems. A few indicators were chosen for the comparison: distances, ridership, costs, Greenhouse Gases (GHG), emissions and population’s perception. The ridership dropped, however, for being “demand-tailored”, the mileage per passenger reduced, improving the costs and GHG emissions. In regards to population’s perception, the system enjoyed a good evaluation.
Find the Thredbo presentation of Felipe Coutinho HERE and the paper HERE
Willingness to share rides in on-demand services for different market segments
The impact of on-demand urban transport services on traffic reduction will depend on the willingness to share (WTS) of individuals. However, the extent to which individuals are willing to share remains largely unknown. By means of a stated preference experiment, this study analyses the WTS of respondents by comparing their preferences towards individual and pooled rides. Urban Dutch individuals are the target population of this study. In our research, we: 1) quantify the WTS in on-demand services with different number of passengers to disentangle the sharing aspect from related time-cost considerations (e.g. detours); 2) investigate which distinct (latent) market segments exist in regards to the WTS and value of time (VOT) for these on-demand services, and 3) analyse which socioeconomic characteristics and travel patterns can help explain taste variations. Despite the large majority of current on-demand rides being individual, we found that less than one third of respondents have strong preferences for not sharing their rides. Also, we found
heterogeneity not only in the values of the WTS of individuals, but also in the way this disutility is perceived (per-ride or proportional to the in-vehicle time).
Find the Thredbo presentation of Maria Alonso-Gonzalez HERE
Walking and bicycle catchment areas of tram stops: factors and insights
Pollution and congestion are important issues in urban mobility. These can potentially be solved by multimodal transport, such as the bicycle-transit combination, which
benefits from the flexible aspect of the bicycle and the wider spatial range of public transport. In addition, the bicycle can increase the catchment areas of public transport stops. Most transit operators consider a fixed 400m buffer catchment area. Currently, not much is known about what influences the size of catchment areas, especially for the bicycle as a feeder mode.
Bicycles allow for reaching a further stop in order to avoid a transfer, but it is not clear whether travelers actually do this.This paper aims to fill this knowledge gap by assessing which factors affect feeder distance and feeder mode choice. Data are collected by an on-board transit revealed preference survey among tram travelers in The Hague, The Netherlands. Both regression models and a qualitative analysis are performed to identify the factors that influence feeder distance and feeder mode choice. Results show that the median walking feeder distance is 380m, and the median cycling feeder distance is 1025m. The tram stop density and chosen feeder mode are most important in feeder distance. For feeder mode choice, the following factors are found to be influential: tram stop density, availability of a bicycle, and frequency of cycling of the tram passenger. Furthermore, the motives of respondents for choosing a stop further away are mostly related to the quality of the transit service and comfort matters, of which avoiding a transfer is named most often. In contrast, the motives for cycling relate mostly to travel time reduction and the built environment. Three important barriers for the bicycle-tram combination have been discovered: unavailability of a bicycle, insufficient and unsafe bicycle parking places. Infrequent users of the bicycle-tram combination are more inclined to travel further to a stop that suits them better.
Find the MT-ITS paper and presentation of Lotte Rijsman HERE and HERE
Understanding the difference in travel patterns between docked and dockless bike-sharing systems: a case study in Nanjing, china
The co-existence of dockless and traditional docked bike-sharing systems presents new opportunities for sustainable transportation in cities all over the world, both serving door to door trips and access and egress to and from transit. To compare travel patterns of these two systems, we explored the GPS data of a dockless bike-sharing scheme and the smart card data of a docked bike-sharing scheme in the city of Nanjing, China over the same time period. In order to obtain information from different perspectives, such as user perception and opinions, an intercept survey on bike-sharing mode choice was conducted. A mode choice model was estimated to reveal the effects of personal information, user perception and experience on bike-sharing usage. Results show that dockless bike-sharing systems have a shorter average travel distance and travel time but a higher use frequency and hourly usage volume compared to docked bike-sharing systems. Trips of docked and dockless bike-sharing on workdays are more frequent than those on weekends, especially during the morning and evening rush hours from 7:00-9:00 and 17:00-19:00, respectively. As to the factors influencing travelers’ mode choice, results show that retirees, enterprise staff and users with E-bikes are less likely to use docked sharing-bikes than dockless bikes. In contrast, high-income travelers and people who are highly sensitive to discounts, internet technology and online payment service are more likely to use the dockless bike-sharing. Finally, policy implications are discussed for cities to improve the performance of docked and dockless bike-sharing systems.
Find our poster HERE
Insights into factors affecting the combined bicycle-transit mode
The combination of bicycle and transit is an upcoming, sustainable multimodality. The flexibility of the bicycle combined with the speed and comfort of good transit can be a highly competitive alternative to the car. This study shows that many factors influence the uptake and attractiveness of the bicycle-transit combination. An in-depth literature review resulted in over thirty unique factors: six transit related factors, twenty first-last mile factors and fifteen context related factors. All these factors might influence the demand for this ‘new’ mode positively or negatively. An exploratory choice modelling study showed that Dutch bicycle-train users in our sample are willing to pay €0.11 for a minute less bicycle time, €0.08 for a minute less train time, €0.11 for a minute of less time to park and €0.60 per avoided transfer. These kinds of insights give the bicycle and transit sector valuable information to be used in modelling multimodality and cost-benefit analyses, thereby supporting improved decision making and integrated design of bicycle and transit networks.
Read the full CASPT paper HERE and find the presentation HERE
Wat gaat MaaS ons brengen?
MaaS congres 2018: Niels van Oort is assistant professor public transport aan de TU Delft en doet onderzoek naar de effecten van nieuwe vervoerssytemen. Hij gaat de mogelijke impact van MaaS op reizigers en maatschappij toelichten, met voorbeelden van verschillende pilots en onderzoeken.
Zie HIER zijn bijdrage aan het MaaS congres 2018
Nieuwe lessen over de potentie van Fiets en OV
Het combineren van fiets en openbaar vervoer is een duurzame oplossing voor de (mobiliteits)uitdagingen in zowel stedelijke gebieden als daarbuiten. Er is een revival van de fiets gaande en ook hoogwaardig openbaar vervoer rukt op. De keten van fiets mét openbaar vervoer combineert de voordelen van beide systemen: De fiets zorgt voor fijnmazige ontsluitingen van herkomst en bestemmingen, is milieuvriendelijk en stimuleert een gezonde leefstijl. Voor wat betreft OV neemt de kwaliteit de laatste jaren sterk toe door de introductie van hoogwaardig OV (HOV): snelle, frequente en betrouwbare bus- tram- en metrolijnen met een hoog comfortniveau. Voorbeelden zijn R-Net, Randstadrail en Q-Link. De halteafstanden van deze systemen zijn relatief hoog, waardoor de fiets een belangrijke rol speelt in de gebiedsontsluiting.
Om het succes van de fiets en OV verder uit te bouwen is kennis nodig over hoe de mobilist zich nu en in de toekomst beweegt: Wat zijn de succesfactoren, welke voorwaarden spelen een rol en waarom worden bepaalde keuzes gemaakt, bijvoorbeeld. Dit paper laat de resultaten zien van vier TU Delft onderzoeken op dit gebied. Belangrijkste, nieuwe inzichten zijn bijvoorbeeld dat het invloedsgebied van HOV haltes tot 4x groter is ten opzichte van “gewoon’’ OV. Verder blijkt dat treinreizigers bereid zijn ca. 6 min. extra te fietsen naar een station waar ze een directe trein kunnen nemen naar hun bestemming (in plaats van met een overstap). Tot slot blijkt dat de huidige groep fiets-OV’ers in te delen is in 7 groepen, waarvan de middle-aged male professionals de grootste zijn en de gepensioneerden de kleinste. De resultaten zijn de basis voor verder onderzoek en toepassing om te komen tot een optimaal Fiets-OV netwerk.
Lees het hele CVS paper HIER
De presentatie is HIER beschikbaar
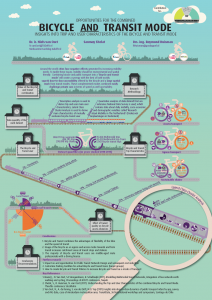
Opportunities for the Combined Bicycle and Transit Mode
Around the world cities face negative effects generated by increasing mobility needs. To tackle these issues, mobility should be environmental and spatial friendly. Combining bicycle and public transport into a ‘bicycle + transit mode’ will create a synergy with the best of both worlds: superb door-to-door accessibility offered by the bicycle and a large spatial reach from transit modes. These complemented modes combined easily challenge private carsin terms of speed as well accessibility.
Research regarding the users and trip types of the bicycle and transit mode is largely missing. This is unfortunate, since understanding both user and trip characteristics is of the utmost importance to improve the share of the bicycle and transit mode. Policy-makers can make concrete decisions on infrastructure and service investments only when the gap between the aforementioned societal need and scientific knowledge is filled.
The main analysis in the study is based on data from the Netherlands. The Netherlands is one of the countries with a head start regarding the use of the bicycle + transit mode. A one-day trip diary survey, representative of the population of the Netherlands, with more than 250,000 respondents who made nearly 700,000 trips over the course of 6 years (2010-2015), is used to derive important trip and user characteristics of the bicycle + transit mode. Finally, latent class cluster analysis is applied to find prototypical users of this mode on the basis of their socio-demographic attributes.
It is, for example, found that the most important purposes of the bicycle and transit mode are work or education, typically involving relatively long distances. Bicycle and transit-potential for other transit network levels, such as metros and bus rapid transit can be found. Moreover, seven unique user groups – from middle-aged professionals to school children – are identified, and their different travel behaviour is discussed.
Urban Demand Responsive Transport in the Mobility as a Service ecosystem: its role and potential market share
Mobility as a Service (MaaS) is entering the transportation market. MaaS aims at the full
integration of the existing transportation services and it offers tailored mobility packages to
the user. In MaaS ecosystems, on-demand services play an important role as complement to
public transport due to their flexibility. However, to date, most attention has been placed on
individual on-demand services. This study focuses on Demand Responsive Transport (DRT):
collective on-demand services. Using an on-line survey, we analysed the characteristics of
the respondents who chose different modes of transport among their selected modes.
Results find a distinctive pattern in the willingness of users to use different modes, with
different levels in what could be considered as a multimodality ladder. The different rungs of
it would be: 1st car (if available), 2nd public transport, 3rd DRT and 4th taxi-like services.
This way, a person standing on the third rung would include car, public transport and DRT in
their consideration set, but not taxi. This finding suggests that, if implemented in the right
way, DRT services can attract a larger number of users than taxi-like services, especially in a
MaaS ecosystem where initial barriers to try this service can be lessened.
Find the paper presented by Maria Alonso Gonzalez at the Thredbo conference in Stockholm HERE