Posts in category Papers
Inclusive mobility
Learn more about our research and findings regarding inclusive mobility:
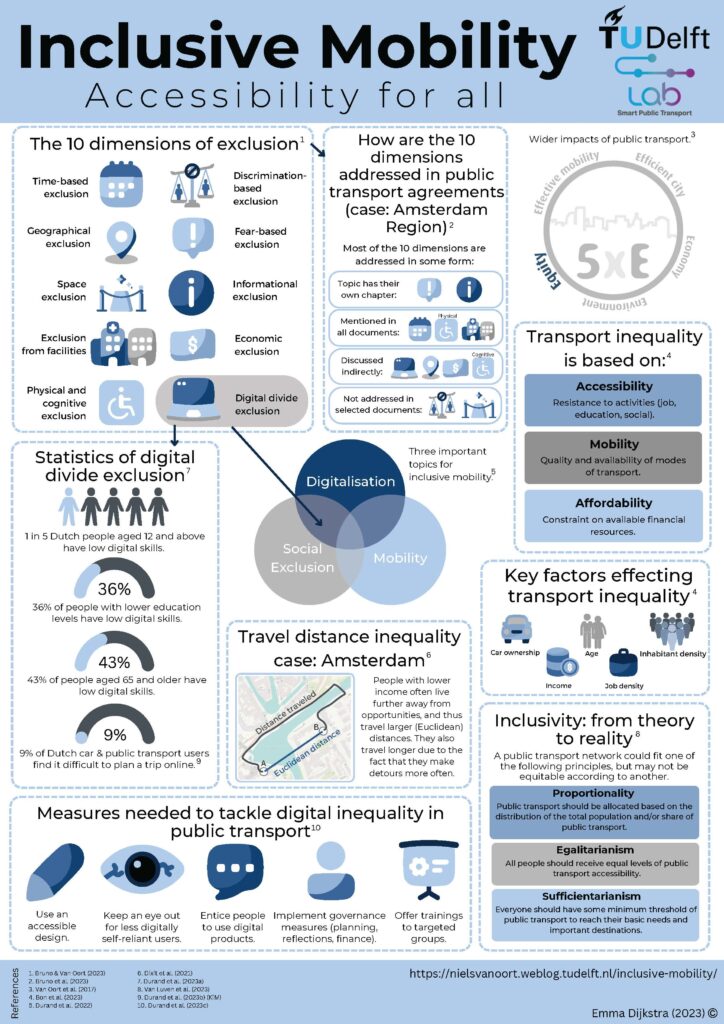
Download the infographic HERE
References
- Bruno, M., and N. Van Oort (2023) The ten dimensions of transport related social exclusion, position paper
- Bruno, M., Kouwenberg, M., & van Oort, N. (2024). Evaluating How Transportation Policy Addresses Transport Related Social Exclusion: A Novel Method Applied to the Amsterdam Transport Region. Transportation Research Interdisciplinary Perspectives, Volume 26.
- Van Oort, N., R.A.J. vd Bijl, F.C.A. Verhoof (2017), The wider benefits of high quality public transport for cities, European Transport Conference, Barcelona.
- Bon, T., Bruno, M., & van Oort, N. (2025). Three-dimensional transport poverty and its socio-demographic and urban density predictors: Spatial regression analyses of neighborhoods in the Amsterdam metropolitan area. Transportation Research Interdisciplinary Perspectives.
- Durand, A., Zijlstra, T., van Oort, N., Hoogendoorn-Lanser, S., & Hoogendoorn, S. (2022) Access denied? Digital inequality in transport services, Transport Reviews, 42:1, 32-57
- Dixit M., Chowdhury S., Cats O., Brands T., van Oort N. and Hoogendoorn S. (2021). Examining circuity of urban transit networks from an equity perspective, Journal of Transport Geography, Volume 91, 102980.
- Durand, A., Zijlstra, T., Hamersma, M., van Oort, N., Hoogendoorn-Lanser, S., & Hoogendoorn, S. (2023). “Who can I ask for help?”: Mechanisms behind digital inequality in public transport. Cities, 137, 104335
- Van Luven, M., N. van Oort, O. Cats, M. Bruno, M. Kouwenberg (2023), How to achieve an equitable distribution of accessibility by evaluating and modifying public transport networks: a comparison of accessibility distribution principles in the Netherlands, European Transport Conference, Milano.
- Durand, A., Hamersma, M., Rienstra, S. (2023). Use and perceived effects of digital travel information for car and public transport travel. Brochure. The Hague: Netherlands Institute for Transport Policy Analysis (KiM).
- Durand, A., Zijlstra, T., Hamersma, M., van Oort, N., Hoogendoorn-Lanser, S., & Hoogendoorn, S. (2023). Fostering an inclusive public transport system in the digital era: an interdisciplinary approach. Transportation Research Interdisciplinary Perspectives, Volume 22, 100968.
Overview integrated Bicycle+Transit research
One sustainable mode gaining more attraction recently is the bicycle-transit combination: with a bicycle ride before and/or after the public transport journey. Integrating these modes, both short and long distances from door-to-door can be covered fast and comfortable (thanks to transit) and flexible (due to the bike). This makes the bicycle-transit combination a potential competitor for the car. In addition, the effectiveness of public transport will substantially increase due to increased catchment areas and enhanced first and mile options. However, integrating both modes is not easy and knowlegde about planning, behaviour and implementation are limited. We started our research in this domain back in 2015 and then provided many insights since then, provided in classic journal papers, but we also put much effort in other formats, suiting better to all needs. Learn more about planning, modelling and operating an integrated bicycle+transit system via the contributions below:
Podcasts
The bicycle and transit combination, Dutch Cycling Embassy
Designing optimal Public Transport and shared modes, Mobility Innovators
Video
Integrating cycling and transit, EIT Urban Mobility
Infographics
Micromobility and public transport
Blog
The Bicycle-Train Combination: A Ticket to Success, Dutch Cycling Embassy
Journal papers
Brown, A., N. van Oort (2026), Strategies, opportunities, and challenges of integrating shared micromobility with public transport, Transportation Research Part D: Transport and Environment,
Volume 151,
Geržinič, N., M. van Hagen, H. Al-Tamimi, D. Duives, N. van Oort (2026), How do activity-end trip characteristics affect the choice for shared micromobility? A latent class choice modelling approach for train station egress trips in the Netherlands, Transportation Research Part A: Policy and Practice, Volume 204.
Van Kuijk, R.J., T.H.A. de Ridder, N. van Oort, G. Homem de Almeida Correia, B. van Arem (2025),
Redesign of public transit in low-demand areas, and integration with shared modes, based on travel preferences: A case study analysis in the province of Utrecht, the Netherlands, Case Studies on Transport Policy, Volume 22.
Geržinič, N., M. van Hagen, H. Al-Tamimi, N. van Oort, D. Duives (2025),
Drivers and barriers to integrating shared micromobility with public transport A latent class clustering analysis of adoption attitudes in the Netherlands, Journal of Cycling and Micromobility Research, Volume 6.
Mbugua, W., D. Duives, J.A. Annema, N. van Oort (2025), Societal costs and benefits analysis of integrating bike-sharing systems with public transport: A case study of the public transport bike (‘OV-fiets’) in the Netherlands, Case studies on transport policy.
Spierenburg, L., H. van Lint, N. van Oort (2024), Synergizing cycling and transit: Strategic placement of cycling infrastructure to enhance job accessibility, Journal of Transport Geography, Volume 116.
Xanthopoulos, S., M. van der Tuin, S. Sharif Azadeh, G. Correia, N. van Oort, M. Snelder (2024), Optimization of the location and capacity of shared multimodal mobility hubs to maximize travel utility in urban areas, Transportation Research Part A: Policy and Practice, Volume 179.
Van Kuijk, R.J., G. Homem de Almeida Correia, N. van Oort, B. van Arem (2023), Preferences for first and last mile shared mobility between stops and activity locations: A case study of local public transport users in Utrecht, the Netherlands, Transportation Research Part A: Policy and Practice, Volume 166.
Montes, A., N. Geržinic, W.V. Veeneman, N. van Oort, S.P. Hoogendoorn (2023), Shared micromobility and public transport integration – A mode choice study using stated preference data, Research in Transportation Economics, Vol. 99, 101302.
Torabi, F., Y. Araghi, N. van Oort, S.P. Hoogendoorn (2022), Passengers preferences for using emerging modes as first/last mile transport to and from a multimodal hub case study Delft Campus railway station, Case Studies on Transport Policy, Vol.10, Issue 1, pp.300-314.
Liouta, G., Saibene, G., van Oort, N., Cats, O., & Schulte, F. (2022). Can Shared Mobility Compensate for Public Transport Disruptions? The Case of Milan’s Bike Sharing System During the COVID-19 Pandemic. Transportation Research Record.
Van Marsbergen, A., D. Ton, S. Nijënstein, J.A. Annema, N. van Oort (2022), Exploring the role of bicycle sharing programs in relation to urban transit, Case Studies on Transport Policy, Volume 10, Issue 1.
Stam, B., van Oort, N., van Strijp-Harms, H.J., Van der Spek, S., Hoogendoorn, S.P. (2021). Travellers’ preferences towards existing and emerging means of first/last mile transport: a case study for the Almere centrum railway station in the Netherlands. Eur. Transp. Res. Rev. 13, 56. .
Bronsvoort K, Alonso-González M, Van Oort N, Molin E, Hoogendoorn S. (2021). Preferences toward Bus Alternatives in Rural Areas of the Netherlands: A Stated Choice Experiment. Transportation Research Record. 2675(12):524-533.
Ton, D., Shelat, S., Nijënstein, S., Rijsman, L., van Oort, N., Hoogendoorn, S. (2020) Understanding the Role of Cycling to Urban Transit Stations through a Simultaneous Access Mode and Station Choice Model, Transportation Research Record, 2674 (8), pp. 823-835.
Ma, X., Ji, Y., Yuan, Y., Van Oort, N., Jin, Y., Hoogendoorn, S.(2020), A comparison in travel patterns and determinants of user demand between docked and dockless bike-sharing systems using multi-sourced data, Transportation Research Part A: Policy and Practice, 139, pp. 148-173.
Ma, X., Yuan, Y., Van Oort, N., Hoogendoorn, S., (2020). Bike-sharing Systems: Impact on Modal Shift: A Case Study in Delft, the Netherlands. J. Clean. Prod. 120846.
Van Mil, J.F.P., Leferink, T.S., Annema, J.A. et al. Insights into factors affecting the combined bicycle-transit mode. Public Transport (2020).
Rijsman, L., N. van Oort, D. Ton, S. Hoogendoorn , E. Molin, T. Teijl (2019), Walking and bicycle catchment areas of tram stops: factors and insights, Proceedings of IEEE MT-ITS conference, Krakow.
Shelat, S., R. Huisman, N. van Oort (2018). Analysis of the trip and user characteristics of the combined bicycle and transit mode. Research in Transportation Economics.
Brand, J., N. van Oort, B. Schalkwijk, S. Hoogendoorn (2017), Modelling Multimodal Transit Networks; Integration of bus networks with walking and cycling, MT-ITS Conference Napoli.
Mobility hubs: Why, who, how?
Mobility hubs are often presented as the solution for enhanced accessibility, a shift towards sustainable mobility and/or improved public space. Sometimes, they seem to be a goal in itself.
In our research, we try to find out how to achieve the mobility, spatial and societal goals by investigating the potential users and their needs, and the required offered modes and facilities accordingly.
The highlights of multiple research projects are presented the infographic below. More details and extra insights are available via the related research papers.

References
- Hoogenboom (2024), Exploiting the benefits of a mobility hub to incentivize shared car usage.
- Montes, A., N. Geržinic, W.V. Veeneman, N. van Oort, S.P. Hoogendoorn (2023), Shared micromobility and public transport integration – A mode choice study using stated preference data, Research in Transportation Economics, Vol. 99, 101302.
- Spierenburg, L., H. van Lint, N. van Oort (2024), Synergizing cycling and transit: Strategic placement of cycling infrastructure to enhance job accessibility,
Journal of Transport Geography, Volume 116. - Van der Meer, T. Leferink, N. Geržinič, J. A. Annema and N. v. Oort (2023), Identifying potential use of emerging neighbourhood mobility hubs using behavioural modelling, 8th International Conference on Models and Technologies for Intelligent Transportation Systems (MT-ITS), Nice, pp. 1-6.
- Van Gerrevink, I., J. de Jong, N. van Oort (2021), Ex-post evaluatie van mobiliteitshubs: Een kwalitatieve studie naar de factoren die het gebruik en de effecten van mobiliteitshubs beïnvloeden. CVS congres Utrecht. (in Dutch; English report)
- Van Kuijk, R.J., G. Homem de Almeida Correia, N. van Oort, B. van Arem (2023), Preferences for first and last mile shared mobility between stops and activity locations: A case study of local public transport users in Utrecht, the Netherlands, Transportation Research Part A: Policy and Practice, Volume 166.
- Vianen, J., N. van Oort, M. Walvius (2022) Een wijkhub voor iedereen? Inzichten in de behoefte aan hubfaciliteiten en deelmobiliteit voor verschillende bevolkingsgroepen. CVS congres Utrecht (in Dutch; English report)
- Xanthopoulos, S., M. van der Tuin, S. Sharif Azadeh, G. Correia, N. van Oort, M. Snelder (2024), Optimization of the location and capacity of shared multimodal mobility hubs to maximize travel utility in urban areas, Transportation Research Part A: Policy and Practice, Volume 179.
Ontsluitend ov
Dit weekend schreef Joost van Velzen in Trouw over de Hugohopper, een succesvol vervoerssysteem in de gemeente Dijk en Waard, dat naast bereikbaarheid ook voorziet in sociale cohesie.
De Hugohopper is een mooi voorbeeld van lokaal maatwerk voor de bereikbaarheid van minder drukke gebieden, als alternatief voor de ontsluitende bus. Aandachtspunt is wel integratie van informatie en betaling met gewoon ov, om ook bezoekers te faciliteren. De inzet van vrijwilligers is een kracht, maar kan op termijn ook een uitdaging vormen.
Het voorbeeld laat goed zien dat voor minder drukke gebieden en -tijden geen standaard ov-oplossing bestaat om geografische uitsluiting te voorkomen. In sommige gevallen volstaat de gewone bus, maar de buurtbus, flex-ov of bijvoorbeeld vervoer via verenigingen, zoals de HugoHopper, zijn soms betere oplossingen voor inclusieve mobiliteit. In ons onderzoek proberen we te begrijpen welk systeem waar en wanneer de beste oplossing biedt, passend bij de behoeften en kenmerken van de gebruikers én de maatschappelijke doelen en restricties.
Lees meer over ons onderzoek over ontsluitend ov en inclusieve mobiliteit:
Inclusive mobility, accessibility for all, infographic and papers
Bruno et al. (2024), Evaluating How Transportation Policy Addresses Transport Related Social Exclusion: A Novel Method Applied to the Amsterdam Transport Region
Geržinič et al. (2023), What is the market potential for on-demand services as a train station access mode?
Bronsvoort et al. (2021). Preferences toward Bus Alternatives in Rural Areas of the Netherlands: A Stated Choice Experiment.
Coutinho et al.(2020), Impacts of replacing a fixed public transport line by a demand responsive transport system: Case study of a rural area in Amsterdam
Subsidie voor onrendabele lijnen op het platteland?, Brabants Dagblad
Stijgende vervoersarmoede, KRO/NCRV Lief Gebaar
Minder bushaltes alléén niet gelijk aan minder bereikbaarheid, OV Magazine
Wegvallen busritten heeft grote gevolgen voor deze GGZ-instelling, EenVandaag
Minder reizigers door Flexvervoer hoeft niet erg te zijn, OV Pro
MT-ITS conference: Identifying potential use of emerging neighbourhood mobility hubs using behavioural modelling
Neighbourhood mobility hubs may play an important role in mitigating the impact of passenger cars on climate change and urban public space. As a relatively new concept, academic research on the user potential of neighbourhood mobility hubs is so far limited. This research aims to identify which user groups are likely to adopt services offered by a neighbourhood mobility hub. A survey was distributed in the Netherlands (N=298) and an Exploratory Factor Analysis (EFA) and a Latent Class Cluster Analysis (LCCA) were executed. Four distinctive groups of intended users were uncovered. Two of the clusters have intentions to use neighbourhood mobility hubs. The other two identified clusters do not (yet) intend to use neighbourhood mobility hubs. The clusters indicate that people who currently already travel more by sustainable modes (train or (e-)bicycle) are more likely to be adopters of neighbourhood mobility hubs than the traditional car users. In practice, this may make the positive effect of hubs more limited than anticipated or even increase car use. However it could also facilitate those travelling sustainable to do so for longer as additional shared modes become available to them via hubs. Limitations and directions for further research are discussed.
Read the paper of Van der Meer et al. (2023) HERE
Find the presentation of MT-ITS (2023) in Nice HERE
The full research report is available HERE
More insights into mobility hubs and shared mobility:
PhD project: Robust train trajectory optimization
In cooperation with the Dutch Railways (NS), Alex Cunillera works in this PhD research on robust train trajectory optimization. Even two trains of the same model running on the same line show significant differences in their dynamics. This might be due to different passenger loads, weather, fault history, driving style of the train driver, etc. Moreover, there are uncertainties in the track data that may also have a strong influence on the train operation. This research focuses on determining the uncertainties and stochastics of these variations and developing methods to compute robust train trajectories that optimize the energy consumption and minimize delays in the presence of the mentioned variations.
Project contributions (ongoing):
Papers:
Train motion model calibration: research agenda and practical recommendations (ITSC 2022)
Presentations:
Real-time train motion parameter estimation using an Unscented Kalman Filter (RailBeijing 2021)
Train motion model calibration: research agenda and practical recommendations (ITSC 2022)
CVS congres 2022
Op het CVS congres 2022 waren de volgende presentaties en papers vanuit het Smart Public Transport Lab:
Een onderzoeksagenda voor sociaal inclusieve mobiliteit in de Vervoerregio Amsterdam, Matthew Bruno, Niels van Oort, Suzanne Kieft: Paper en presentatie(NL) en presentation(English)
De invloed van comfort en veiligheidsgevoel op stationskeuze voor fietsers, Anne Barneveld, Raymond Huisman, Niels van Oort: Paper en presentatie
Een wijkhub voor iedereen? Inzichten in de behoefte aan hubfaciliteiten en deelmobiliteit voor verschillende bevolkingsgroepen, Jarco Vianen, Niels van Oort, Minze Walvius: Paper en presentatie
Covid impacts on train travel behaviour
Delft University of Technology and the Dutch railways (NS) started a joint, longitudinal research in April 2020 on Covid impacts on train passenger behaviour. During the pandemic, 7 surveys in different stages (15,000-45,000 participants each) were held to learn about the impacts and expectations. The main results are presented in an infographic.
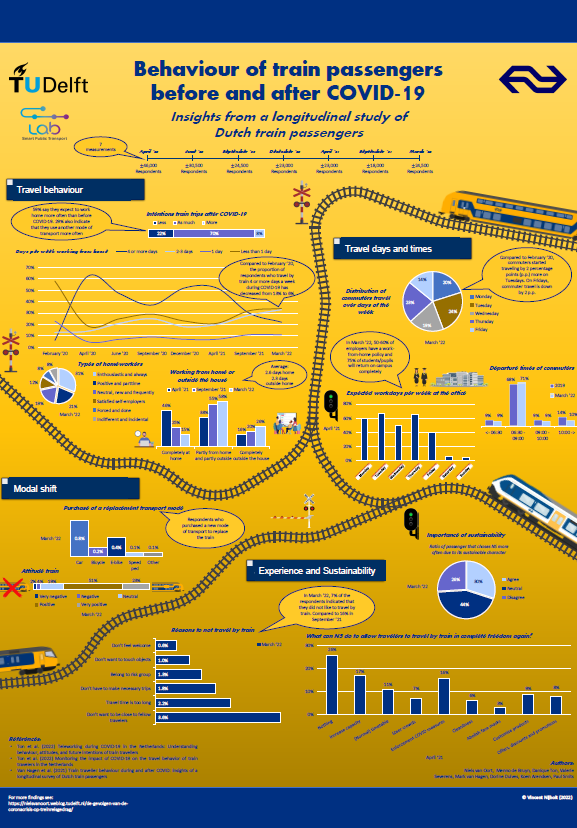
Find the high resolution infographic HERE. Also available in DUTCH
Find the detailed results in these scientific papers:
Transportion research-Part A: Teleworking during COVID-19 in the Netherlands: Understanding behaviour, attitudes, and future intentions of train travellers
Bivec Transport Days: Train traveller behaviour during and after Covid: insights of a
longitudinal survey of Dutch train passengers
Transport Research Procedia: Monitoring the impact of COVID-19 on the travel behavior of train
travelers in the Netherlands
Find other output such as reports, presentations and media articles
Micromobility and public transport
Following technological and societal developments, new modes and services arrive in our cities. Micromobility solutions, such as shared (e-)bikes and –scooters, are adding new opportunities for individuals, but what their (potential) contribution is to societal objectives such as sustainability, land use and inclusiveness, is not yet known. In order to gain this knowledge and optimize the mobility mix, the Smart Public Transport Lab investigates the demand and supply impacts and interaction of micromobility, including the interaction with public transport. In this infographic the main, recent results of the ongoing research are summarized.
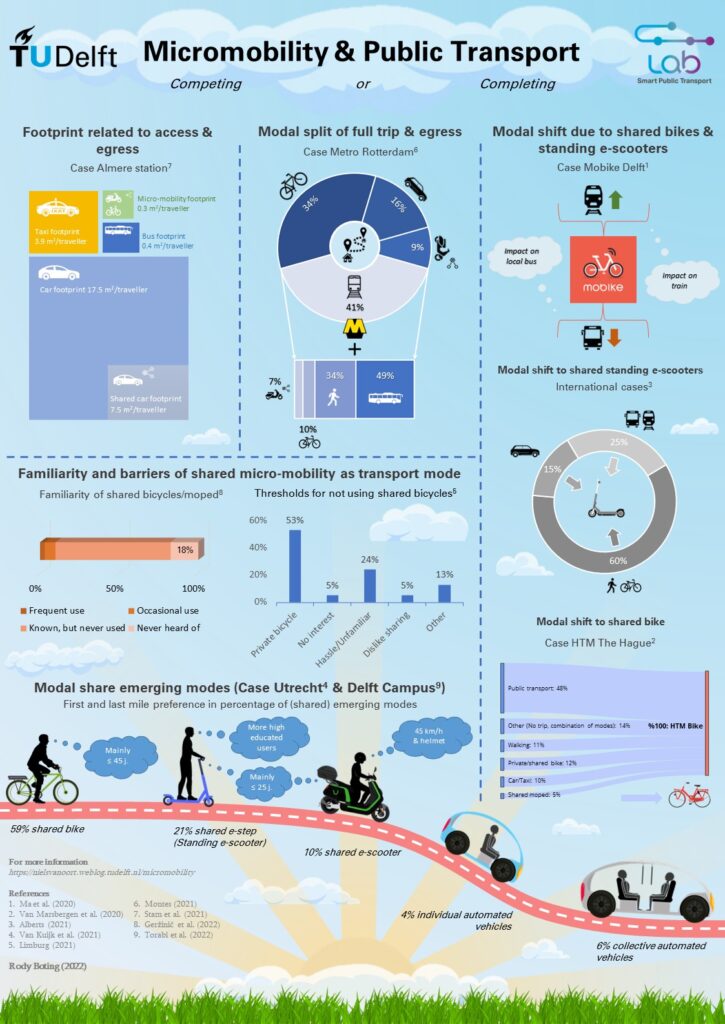
Find more results and details in the related papers and theses:
1. Ma et al. (2020): Bike-sharing systems’ impact on modal shift: A case study in Delft, the Netherlands
2. Van Marsbergen et al. (2022): Exploring the role of bicycle sharing programs in relation to urban transit
3. Alberts (2021): Standing e-scooters, what to expect: micro-mobility with micro effects?
4. Van Kuijk et al. (2022): Preferences for shared modes of local public transport users in the last mile
5. Limburg (2021): Potential for sustainable mode usage amongst car users in mid-sized cities
6. Montes et al. (2023): Studying mode choice in multimodal networks including shared modes
7. Stam et al. (2021): Travellers’ preferences towards existing and emerging means of first/last mile transport: a case study for the Almere centrum railway station in the Netherlands
8. Geržinič et al. (2022): Potential of on-demand services for urban travel
9. Torabi et al. (2022): Passengers preferences for using emerging modes as first/last mile transport to and from a multimodal hub case study Delft Campus railway station
Potential of on-demand services for urban travel (Flex-OV)
On-demand mobility services are promising to revolutionise urban travel, but preliminary studies are showing that they may actually increase the total vehicle miles travelled, thereby worsening road congestion in cities. In this study, we assess the demand for on-demand mobility services in urban areas,using a stated preference survey, to understand the potential impact of introducing on-demand services on the current modal split. The survey was carried out in the Netherlands and offered respondents a choice between bike, car, public transport and on-demand services. 1,063 valid responses are analysed with a multinomial logit and a latent class choice model. By means of the latter, we uncover four distinctive groups of travellers based on the observed choice behaviour. The majority of the sample (55%) are avid cyclists and do not see on-demand mobility as an alternative for making urban trips. Two classes (27% and 9% of the sample) would potentially use on-demand services: the former is fairly timesensitive and would thus use on-demand service if they were sufficiently fast. The latter class however is highly cost-sensitive, and would therefore use on-demand mobility primarily if it is cheap. The fourth class (9%) shows very limited potential for using on-demand services.
Read the paper by Nejc Geržinič HERE
