Niels van Oort
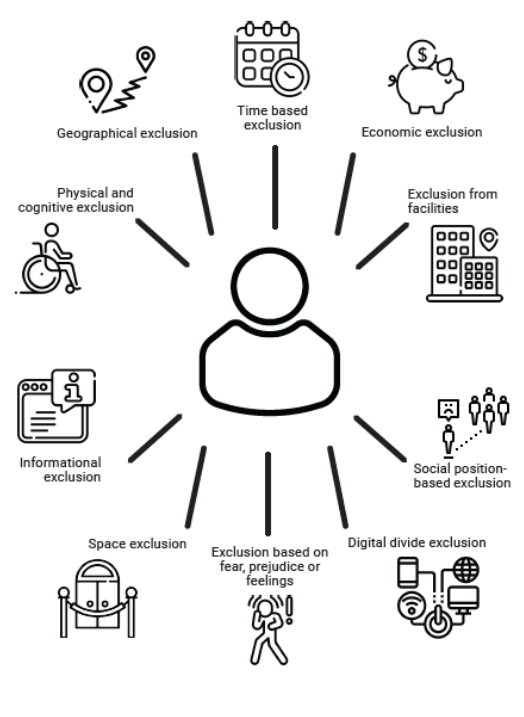
10 dimensions of transport related social exclusion
Transport Related Social Exclusion (TRSE) looks at how people who are socially disadvantaged for reasons such as employment status, income, age, or ability, can face limitations in their ability to access transportation services. As income is only one of these factors, people can experience TRSE without having a low income (Yigitcanlar et al., 2018). Rather, social exclusion is defined by an exclusion from economic life, social services, civic life, and social networks (Spoor, 2013). TRSE looks at how elements of the transportation system contribute to this exclusion (Yigitcanlar et al., 2018).
This figure provides an overview of 10 dimensions of Transport Related Social Exclusion, further explained (incl. references) in the position paper of Bruno and Van Oort (2023).
Impacts of Covid on train traveller behaviour / De gevolgen van de coronacrisis op treinreisgedrag
Delft University of Technology and the Dutch railways (NS) started a joint, longitudinal research in April 2020 on Covid impacts on train passenger behaviour. During and after the pandemic, 8 surveys in different stages (15,000-45,000 participants each) were held to learn about the impacts and expectations.
Read more in the papers, presentations and news releases below. English publications are highlighted in the list.
***
TU Delft en NS zijn 24 april 2020 een grootschalig, longitudinaal onderzoek naar de gevolgen van de coronacrisis op het reisgedrag gestart. In de 8 metingen zijn per keer 15.000-45.000 reizigers bevraagd. Door de intelligente lockdown daalde het aantal treinreizigers in 2020 tot ongeveer 7% ten opzichte van normaal. De onderzoeksvraag is hoe reizigers zich tijdens en na de crisis (verwachten te) gaan gedragen. Vanuit NS zijn Valerie Severens, Menno de Bruyn en Mark van Hagen betrokken bij dit onderzoek. Bij de TU Delft zijn dat Danique Ton, Dorine Duives en Niels van Oort.
Lees hier over het onderzoek en de resultaten tot zover:
<English> The lost passengers: insights into the group of passengers that stopped travelling by train after COVID, European Transport Conference with Menno de Bruyn, Danique Ton and Niels van Oort | Paper | Presentation [Resultaten until November 2022, post-Covid]
De impact van Corona op treinreisgedrag, OV Magazine met Menno de Bruyn en Niels van Oort [Resultaten t/m maart 2022]
“Spitsmijden mislukt, we werken allemaal op dezelfde dag thuis”, OV Pro met Niels van Oort
“Sommige reizigers zijn we gewoon kwijt”, OV Pro met Niels van Oort
<English> Infographic main findings
Infographic met de belangrijkste bevindingen
<English> Change in train travelling behaviour during and after Covid-19 due to anxiety, European Transport Conference with Gudrun Birta Hafsteinsdóttir et al. [Anxiety insights, results until September 2021]
Wegvallen busritten heeft grote gevolgen voor deze GGZ instelling, TV rapportage EenVandaag met Niels van Oort [Resultaten t/m maart 2022]
1 op de 3 busritten dreigt weg te vallen, Artikel EenVandaag met Niels van Oort [Resultaten t/m maart 2022]
Wanneer keren reizigers terug in de trein? ,OV Magazine met Menno de Bruyn en Gudrun Birta Hafsteinsdóttir [Vrijheid om te reizen met de trein, resultaten t/m september 2021]
Treinreizigers blij met afschaffen mondkapjesplicht, OV Magazine met Niels van Oort [Redenen om weer met de trein te reizen, resultaten t/m september 2021]
<English> Effects of anxiety on train travelling behaviour during and after Covid-19, Thesis with Gudrun Birta Hafsteinsdóttir [Results until September 2021]
<English> Teleworking during COVID-19 in the Netherlands: Understanding behaviour, attitudes, and future intentions of train travellers, Paper with Danique Ton et al. [Teleworking profiles and behaviour]
CVS congres presentatie met Danique Ton et al. [Resultaten t/m september 2021]
CVS congres paper met Mark van Hagen et al. [Resultaten t/m april 2021]
<English> Covid and train traveler behavior with Mark van Hagen et al [Paper with results until April 2021]
Hausse aan reizigers verwacht: kun je straks nog zitten in de trein?, NOS met Niels van Oort [Thuiswerken (dagen en frequentie)]
<English> Train traveller behaviour during and after Covid: insights of a longitudinal survey of Dutch train passengers with Mark van Hagen et al. [Paper with results until December]
BNR Nieuwsradio met Niels van Oort [OV ná Corona]
<English> RailTech with Mark van Hagen, Danique Ton and Niels van Oort [results until december + teleworking]
<English> Smart Public Transport Lab COVID webinar met Danique Ton [Teleworking]
Nieuwsuur over toekomst NS met Marjan Rintel [Treinreizen ná Corona]
Verkeerskunde artikel met Valerie Severens, Mark van Hagen, ea [resultaten april, juni en september]
OV Pro artikel met Menno de Bruyn en Niels van Oort [resultaten t/m september]
Interview OV Magazine met Menno de Bruyn
SpoorPro TV met Menno de Bruyn en Niels van Oort (vanaf 16:15 min) [resultaten t/m september]
CVS paper met Mark van Hagen, Dorine Duives en Valerie Severens [resultaten t/m juni]
<English>AET Covid webinar met Mark van Hagen en Niels van Oort [resultaten t/m september]
Fietscommunity presentatie met Niels van Oort [effecten fiets en OV, april en juni]
Presentatie EMTA met Dorine Duives [resultaten t/m juni]
MPN symposium met Mark van Hagen en Danique Ton [resultaten april en juni]
SpoorPro TV met Menno de Bruyn en Niels van Oort [resultaten april]
<English>Webinar ADS met Menno de Bruyn
<English> Webinar Smart Public Transport Lab met Danique Ton [resultaten april]
PhD project: Robust train trajectory optimization
In cooperation with the Dutch Railways (NS), Alex Cunillera works in this PhD research on robust train trajectory optimization. Even two trains of the same model running on the same line show significant differences in their dynamics. This might be due to different passenger loads, weather, fault history, driving style of the train driver, etc. Moreover, there are uncertainties in the track data that may also have a strong influence on the train operation. This research focuses on determining the uncertainties and stochastics of these variations and developing methods to compute robust train trajectories that optimize the energy consumption and minimize delays in the presence of the mentioned variations.
Project contributions (ongoing):
Papers:
Train motion model calibration: research agenda and practical recommendations (ITSC 2022)
Presentations:
Real-time train motion parameter estimation using an Unscented Kalman Filter (RailBeijing 2021)
Train motion model calibration: research agenda and practical recommendations (ITSC 2022)
Inclusief openbaar vervoer, van theorie naar praktijk
Hoewel de theorieën over rechtvaardige mobiliteit niet nieuw zijn, missen we nog wel kennis over de implicaties en toepassing. Monica van Luven van het Smart Public Transport Lab deed bij de Vervoerregio Amsterdam onderzoek. “We staan nog aan het begin van goede inbedding van inclusieve mobiliteit in onze beleidscyclus en moeten nog verschillende belangrijke keuzes maken.”
Lees HIER het hele onderzoek
Het 3-jarige onderzoek van TU Delft en Vervoerregio over inclusieve mobiliteit vind je HIER
Ons onderzoek naar de digitale kloof i.s.m. het Kennisinstituut voor Mobiliteitsbeleid vind je HIER
CVS congres 2022
Op het CVS congres 2022 waren de volgende presentaties en papers vanuit het Smart Public Transport Lab:
Een onderzoeksagenda voor sociaal inclusieve mobiliteit in de Vervoerregio Amsterdam, Matthew Bruno, Niels van Oort, Suzanne Kieft: Paper en presentatie(NL) en presentation(English)
De invloed van comfort en veiligheidsgevoel op stationskeuze voor fietsers, Anne Barneveld, Raymond Huisman, Niels van Oort: Paper en presentatie
Een wijkhub voor iedereen? Inzichten in de behoefte aan hubfaciliteiten en deelmobiliteit voor verschillende bevolkingsgroepen, Jarco Vianen, Niels van Oort, Minze Walvius: Paper en presentatie
Covid impacts on train travel behaviour
Delft University of Technology and the Dutch railways (NS) started a joint, longitudinal research in April 2020 on Covid impacts on train passenger behaviour. During the pandemic, 7 surveys in different stages (15,000-45,000 participants each) were held to learn about the impacts and expectations. The main results are presented in an infographic.
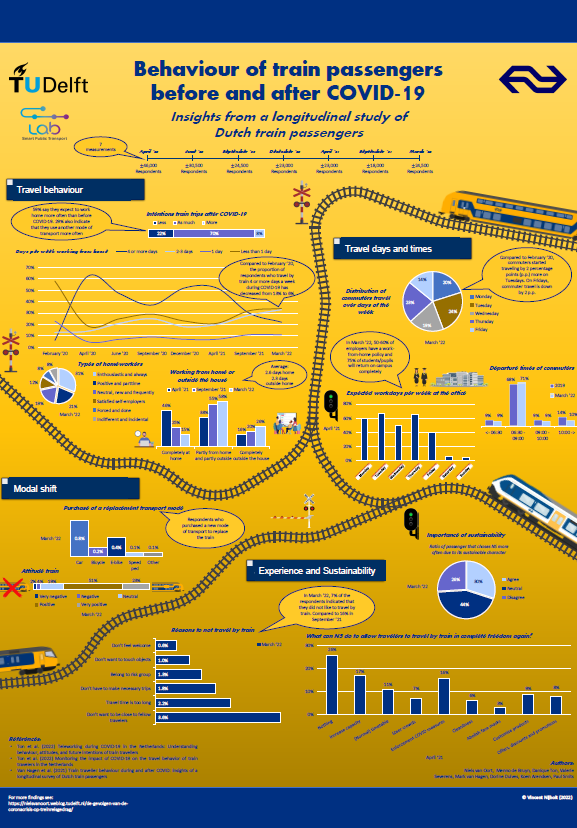
Find the high resolution infographic HERE. Also available in DUTCH
Find the detailed results in these scientific papers:
Transportion research-Part A: Teleworking during COVID-19 in the Netherlands: Understanding behaviour, attitudes, and future intentions of train travellers
Bivec Transport Days: Train traveller behaviour during and after Covid: insights of a
longitudinal survey of Dutch train passengers
Transport Research Procedia: Monitoring the impact of COVID-19 on the travel behavior of train
travelers in the Netherlands
Find other output such as reports, presentations and media articles
Micromobility and public transport
Following technological and societal developments, new modes and services arrive in our cities. Micromobility solutions, such as shared (e-)bikes and –scooters, are adding new opportunities for individuals, but what their (potential) contribution is to societal objectives such as sustainability, land use and inclusiveness, is not yet known. In order to gain this knowledge and optimize the mobility mix, the Smart Public Transport Lab investigates the demand and supply impacts and interaction of micromobility, including the interaction with public transport. In this infographic the main, recent results of the ongoing research are summarized.
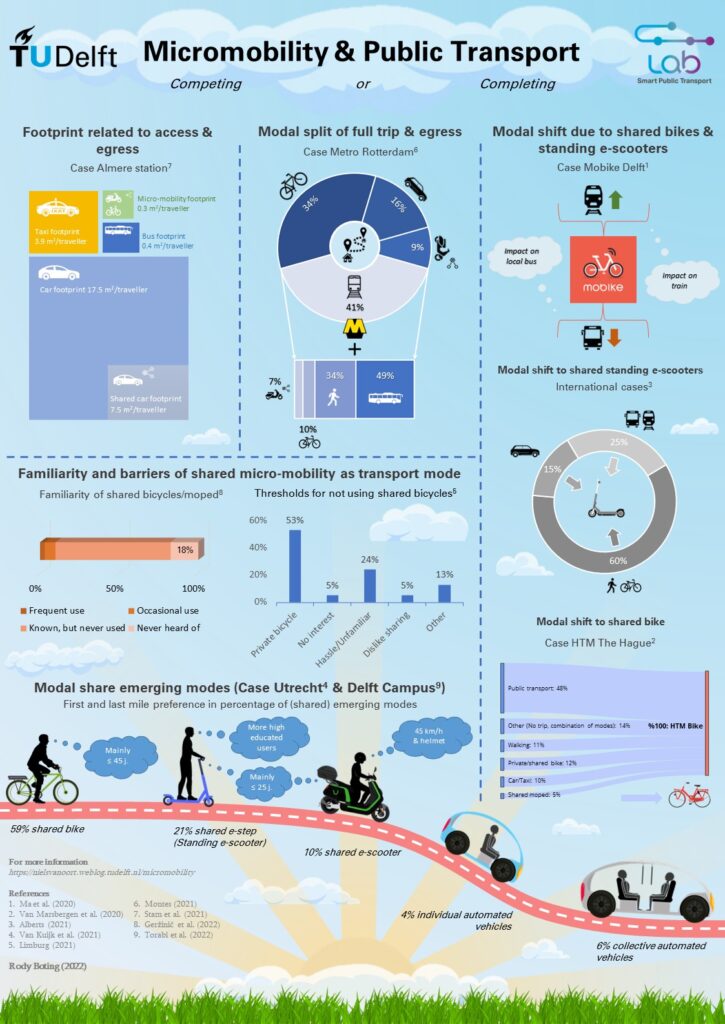
Find more results and details in the related papers and theses:
1. Ma et al. (2020): Bike-sharing systems’ impact on modal shift: A case study in Delft, the Netherlands
2. Van Marsbergen et al. (2022): Exploring the role of bicycle sharing programs in relation to urban transit
3. Alberts (2021): Standing e-scooters, what to expect: micro-mobility with micro effects?
4. Van Kuijk et al. (2022): Preferences for shared modes of local public transport users in the last mile
5. Limburg (2021): Potential for sustainable mode usage amongst car users in mid-sized cities
6. Montes et al. (2023): Studying mode choice in multimodal networks including shared modes
7. Stam et al. (2021): Travellers’ preferences towards existing and emerging means of first/last mile transport: a case study for the Almere centrum railway station in the Netherlands
8. Geržinič et al. (2022): Potential of on-demand services for urban travel
9. Torabi et al. (2022): Passengers preferences for using emerging modes as first/last mile transport to and from a multimodal hub case study Delft Campus railway station
European Transport Conference 2022, Milano
The European Transport Conference (ETC) is taking place this week, September 7-9 2022 in Milano, Italy.
The following Smart PT Lab contributions will be presented:
Change in train travelling behaviour during and after Covid-19 due to anxiety (Presentation and research report)
G.B. Hafsteinsdottir, R. van der Knaap, N. van Oort, M. de Bruyn, M. van Hagen.
Shared micromobility and public transport integration. A mode choice study using stated
preference data (Presentation and research report)
A. Montes Rojas, N. Geržinic, W. Veeneman, N. van Oort, S. Hoogendoorn,.
Understanding the whole station choice concept by cyclists (Presentation and research report)
A Barneveld, R Huisman, N. van Oort.
The full program can be found here:
The future of public transport
Every year in the advanced public transport course, students write an essay on the future of public transport. Passenger association ROVER selects the best one according to the passengers’ perspective. The authors of the winning essay are invited to record a podcast with Geert Kloppenburg in his Metroplitan Podcast series.
2022
Find the winning essay of Hugo Odijk and Tim de Ridder: HERE
Listen to their podcast: HERE
2021
Find the winning essay of Monica van Luven and Stavros Xanthopoulos: HERE
Listen to their podcast: HERE
Student views and research results
Learn more about the views and the research results of our (former) MSc./BSc students in multiple media appearances:
Booklet with all student research stories until 2024 in OV magazine (in Dutch), including student reflections and vision of Jan van Selm.
Janine Grauss, Jorn vd Steen en Yvar de Waaij: Podcast Toekomst van OV en deelmobiliteit op het platteland
Emma Zadeits en Luke Tros: Onderzoeksgroep duurzame mobiliteit groeit bij TU Delft Delft
Tim de Ridder and Hugo Odijk: Podcast Toekomst van het openbaar vervoer
Simone Hoskam: Story of Science video, bicycle+train combination
Monica Van Luven and Stavros Xanthopoulos: Podcast, shared mobility
Tessa Leferink and Joeri van Mil: Blog bicycle+transit combination
Jarco Vianen and Iris van Gerrevink: Verkeersnet TV (in Dutch), mobility hubs
Lara Witte: OV Pro (in Dutch), Covid impacts on public transport
Lucia Bloemendal: OV Magazine (in Dutch), impacts of Covid on mobility
Also check our regular one-pagers in OV Magazine about our research.
